Animation Blog
TECHNIQUES
Persistence of vision: Commonly accepted although controversial
theory about that human eye keeps images of what we see (for about 0.04 second)
and blends them together into motion, it is happening so fast we don’t even
notice it.
However there
is no scientific proof that persistence of vision is real. Scientists prefer to
explain the motion of pictures as phenomena or positive after-images (when
person stares at the light bulb and then turns his head he can still see the
form of the light bulb, so as the images in video/film changes 24 times in a
second we see one image for fraction of
a second and its light stays in our vision and straight after that we see a
following picture and our mind creates a continuity in-between them)
Stop-frame: Animation technique to make an illusion of motion. The
object is moved in small increments between photographed frames, pictures added
together into sequence with the right fps rate would create an illusion of
motion. Stop-frame technique is commonly used with clay, dolls and cut-outs.
Monty Pythons used to use stop-frame techniques for their inserts or intros.
There are also whole movies with just stop-motion, like – Fantastic Mr. Fox,
Chicken Run.
Stop-frame technique also can be
used in a live-action movies. It used to be widely used in early movies as
special effects for monsters or just storytelling as there were no computer
graphics, stop-motion is also in-use in now days live-action movies but it’s
only for the creativity as it is a lot easier to do the effects with the
computer graphics.
Frame rates: No matter of
Persistence of vision or how good is the movement of the object between the
photographs it all comes down to the frame rate of your stop-motion animation.
It is simple to choose, but it’s harder to plan it out, like – how much the object will move in one
second or in example 16 pictures (frames). You can always change fps rate in
post production but if you are doing 10
second animation with a frame rate of 16 fps and you want to change it to 24fps
to get that smoothness, your video will be faster and it’s less then 10 seconds
now, so to change the frame rate to faster you will need more pictures to fill
in the time.
Typically used frame rates in
the industry are:
12 fps. The majority of cartoon animation is drawn on
twos. When put on film, the frames are exposed twice to make 24
fps. In our case, we can simply play back at 12 fps.
15 fps. Less typical would be animation drawn for twos
on video.
24 fps. Film
25 fps. Pal (European) Television.
30 fps. Black and White NTSC (US) Television.
29.97 fps. When color
was added to the television standard, a slight adjustment had to be made to
accommodate the extra signal used for color. The video still plays at 30
fps, but occasionally a frame has to be dropped to keep up. This is
called 'Drop frame'
Techniques:
Traditional 2D animation - begin life as story board, which has
illustrative, drawn images of sequence
and script with comments. This makes easier to plan the plot of animation. The
storyboard artists will have regular meetings with the director where they most
likely going to need to re-board the sequence.
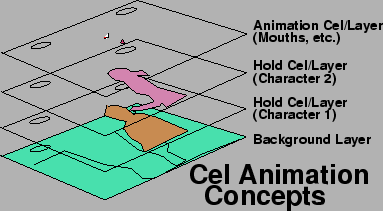
Cel animation – invented in 1915
by Earl Hurd and John Bray. Animation technique that improves the quality of
animation by allowing to keep the background and non-moving objects the same as
they were drawn and stay in the same shape as the animators don’t need to
redraw it for the next frame. For
example – in the animation short, there is two cels, background and character
cel. The character walks in to his room with a bag, and drops it in the corner,
while he was carrying a bag the animator was drawing boys and bag movements.
Now that the bag is not in motion, animator can create a different cel for a
bag and keep it there. So now there is
three cels – background, bag, and character. If the animator would not create
different cel for the bag he would need to draw it every other frame with the
character, and the bag would slightly be changing its shape because it’s
impossible to redraw it exactly the same.
Flick book – a book with series
of pictures that are only slightly different to each other. When the pages are
turned rapidly, it creates an illusion of motion and gives the effect of
animation. Flick book started the
animation centuries ago and is one of the best examples how digital animation
works.
Rotoscoping – drawing or
painting on frames of a movie. Usually using basic colours and only painting
the main elements of a character or object to separate it from the background and
give it an animation detail. The drawing doesn’t have a lot of detail because
it would require a lot of work doing it frame by frame. Rotoscoped objects are
most likely to have a low frame rate.
 Drawn on film – an animation
technique where footage is created by drawing directly on film stock. The
images are created with tools frame by frame, but not taken as pictures in
camera. There are two methods to produce drawn on film animation, one is using
a blank stock, and another is using black (already developed)
Drawn on film – an animation
technique where footage is created by drawing directly on film stock. The
images are created with tools frame by frame, but not taken as pictures in
camera. There are two methods to produce drawn on film animation, one is using
a blank stock, and another is using black (already developed)
Photographic stills – images,
which are taken out of film stock to use as a merchandise to advertise a movie.
But more often, it’s a photo camera taken pictures from filmmaking process, it
can be an artistic picture, where actors are posing. Or it can be a picture
from an actual filmmaking, where the camera, lights and props are visible in
the picture. It has different uses, the artistic picture can be used as a movie
poster. And the filmmaking picture can be used for advertising and letting
people know about an upcoming movie.
Digital techniques:
Application Software:
Flash – one of the most popular
animation application software, most widely being used in internet, as the
flash motion does not take a lot of space and can be uploaded faster than other
application software’s animation. Flash was first used in 1997 for a cartoon series
produced specifically for the internet.
Flash animation software is
widely used between amateurs and professionals,
it’s easy enough to use it for beginners but it also can create more
complex animation with a good quality. Flash animation can integrate bitmaps
and other raster-based art, such as Vector graphics, which can produce clean
graphics appearance.
Anime Studio – is vector-based
2D animation software, started as software called “Moho” in 1999. Anime Studio
is capable of exporting its animation as flash cartoons, and even cut-out style
animation.
It has a lot of useful features
to make an amateurs work easy such as matching sounds to mouth , where the
imported audio can make movements automatically for the characters mouth. Also
features where professionals can experiment and make complex effects with 3D
abilities. Anime studio features layers for different types of artworks and
different layers can be animated.
Development
Pioneers:
Joseph Plateau – In 1832 Joseph
Plateau and his sons, inspired by Michael’s Faraday’s Wheel, made the
Phenakistoscope. Phenakistoscope uses the persistence of motion principle to
create an illusion of motion. Persistence of vision was just a theory, until
1829 when Joseph established it.
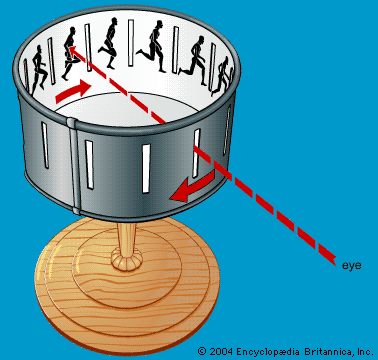 William Horner – invented the Zoetrope,
in 1834. Inspired by Joseph’s Phenakistoscope, built a device also based on
persistence of vision, but Zoetrope did not need a mirror to create an illusion
of motion, and can be viewed by more than 1 person at the same time.
William Horner – invented the Zoetrope,
in 1834. Inspired by Joseph’s Phenakistoscope, built a device also based on
persistence of vision, but Zoetrope did not need a mirror to create an illusion
of motion, and can be viewed by more than 1 person at the same time.
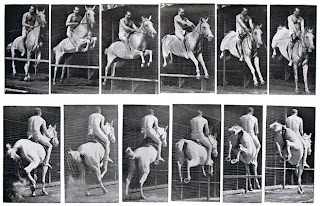
Edward Muybridge – born in 1830,
England. A photographer, that first experimented creating motion, out of single
pictures. In 1881 released a book “The attitudes of animals in motion” with a
series of pictures of animals. Few of those series were made by using 24
cameras that were triggered when the carriage wheels would push the wire as the
horse was moving. It was the first time that some kind of real life activity
was captured in motion. Edward also invented Zoopraxiscope, also known as the
first movie projector, which is a disc with a series of about 12 pictures, when
in movement it creates a motion, through the persistence of vision.
Developers:
 Walt Disney –
born in 1901, America. Walt practised art since early age. After a success
of “Alice Comedies” he became a known
Hollywood figure. In 1932 Disney released his first colour animation “Flowers
and Trees”. Walt and his brother,
co-founder of Walt Disney Company, made most known animation movies in the
history "Cinderella", "The Lion King" and also one of the most known characters - Mickey Mouse. They made the animation popular, which raised people’s interest in
stop-motion industry, and the technologies for animation movies started
advancing.
Walt Disney –
born in 1901, America. Walt practised art since early age. After a success
of “Alice Comedies” he became a known
Hollywood figure. In 1932 Disney released his first colour animation “Flowers
and Trees”. Walt and his brother,
co-founder of Walt Disney Company, made most known animation movies in the
history "Cinderella", "The Lion King" and also one of the most known characters - Mickey Mouse. They made the animation popular, which raised people’s interest in
stop-motion industry, and the technologies for animation movies started
advancing.  Warner Bros.
- established in 1905, America, by four brothers. Warner Bros started as an
independent entertainment company in Hollywood. The feature that made the
company famous in the beginning was – “Where the North Begins” and especially
an actor-dog “Rin Tin Tin”. Warner Bros. are famous for bringing sound into
movies, the idea of actors having a dialog was out there long time, but no
companies did it, rejecting the idea by famous – “Who the heck wants to hear
actors talk?” quote. One of the brothers was suggesting they should have some
dialogs in their features in 1925, after some budget loss in 1926 brother
agreed to give it a try. “The Jazz
Singer” starring Al Jolson, it was only segments of a song and a bit of song
dialog, but it was enough to get people interested and wanting for more
“Talking picture”.
Warner Bros.
- established in 1905, America, by four brothers. Warner Bros started as an
independent entertainment company in Hollywood. The feature that made the
company famous in the beginning was – “Where the North Begins” and especially
an actor-dog “Rin Tin Tin”. Warner Bros. are famous for bringing sound into
movies, the idea of actors having a dialog was out there long time, but no
companies did it, rejecting the idea by famous – “Who the heck wants to hear
actors talk?” quote. One of the brothers was suggesting they should have some
dialogs in their features in 1925, after some budget loss in 1926 brother
agreed to give it a try. “The Jazz
Singer” starring Al Jolson, it was only segments of a song and a bit of song
dialog, but it was enough to get people interested and wanting for more
“Talking picture”.
Len Lye –
born in 1901, New Zealand. Len started his career as an Animator with his
animation movie “Tusalava” in 1929. “Tusalava” was an animation of 4000
separate drawings, it was a not-concrete animation. Len Lye didn’t receive a
lot or recognition for his art so he tried experimenting with technical side of
movie art – painting directly onto celluloid. That was the technique that Len
pioneered. Later on Len combined his technique with an actual footage in “Trade
Tattoo”.
Contemporary Animators:
Terry Gilliam
(Monty Python) – Born 1940, in US. Started his career as an animator and strip cartoonist.
Moving to England Terry created animated sequences for the children series “Do
Not Adjust Your Set”. In the beginning
of the Monty Pythons Flying Circus Gilliam was only a part of the crew,
credited as an animator, later he became a full member of the Monty Pythons.
His animation linked the sketches together. Later the style of his animation (his
own drawn elements with bulbous shapes, backgrounds, moving cut outs from
antique photographs) became an important part of Monty Python style.
 Trey Parker
and Matt Stone – Started their career while in University with an animation
short “Jesus vs. Frosty” which raised some interest so Matt and Trey created a
sequel called “Jesus vs. Santa”. But the animation that made them known was
“The Spirit of Christmas”. The tape went around in different cities where
finally got to hands of Doug Herzog in Comedy Central who asked Trey and Matt
to develop a show. The show was called South Park, with 13 episodes in the
first season. The first shorts and the
pilot episode of South Park were cut-out animation, but then it switched to
computer animation keeping the style of cut-out animation to keep the original
look but to save time producing it.
Trey Parker
and Matt Stone – Started their career while in University with an animation
short “Jesus vs. Frosty” which raised some interest so Matt and Trey created a
sequel called “Jesus vs. Santa”. But the animation that made them known was
“The Spirit of Christmas”. The tape went around in different cities where
finally got to hands of Doug Herzog in Comedy Central who asked Trey and Matt
to develop a show. The show was called South Park, with 13 episodes in the
first season. The first shorts and the
pilot episode of South Park were cut-out animation, but then it switched to
computer animation keeping the style of cut-out animation to keep the original
look but to save time producing it.
Jamie Hewlett
– Became known for his comic “Tank Girl” in Deadline magazine. Comic was
heavily influenced by punk visual art. After the success of Tank Girl, Jamie
did covers of records releases for bands – Senseless things and Cud. By 1992
Jamie became a major creator in comics industry. Few years later Hewlett moved
into a flat with Damon Albarn, it was when they came up with the idea of
virtual band Gorillaz. Albarn would work on the music and Hewlett would come up
with character designs. First album came out in 2000 “Gorillaz”. Hewlett is
most known for his unique character designs of Gorillaz. He also does the
animation for Gorillaz video clips.
2D animation genres and forms
TV – 2D in
television is still quite strong, considering that 2D animation has almost left
the cinema. Most popular animation in TV is cartoons which are likely to stay
in 2D for budget and quality reasons. 3D animation is more popular and
appealing to the audience these days, but to make a good quality 3D animation
few times a week for about 20 minutes would require a big crew and more money.
So the cartoons stay in 2D because it is still attractive to the audience and
it is a traditional way of cartoons, which is going to stay for a long time
because for a lot of people that’s what cartoons are – 2D animation.
 Channel
idents – Most of them nowdays are a mixture of actual footage with the visual
effects that help make it more interesting and help to set the mood. Rarely any
2D animation graphics are used in channel idents, usually only for logos of the
channel.
Channel
idents – Most of them nowdays are a mixture of actual footage with the visual
effects that help make it more interesting and help to set the mood. Rarely any
2D animation graphics are used in channel idents, usually only for logos of the
channel.
Websites – a
lot of websites use flash animation because it is easy to use and makes the
website more attractive for people, with simple things like where you move your
mouse cursor on some kind of option and it opens up without clicking with other
options. When you go to a website and the logo of the website does its ident
introducing itself.
Kornelijus Stanaitis
Reference:
Date accessed
[08/05/12] http://www.mediacollege.com/glossary/p/persistence-of-vision.html
Date accessed
[08/05/12] http://www.grand-illusions.com/articles/persistence_of_vision/
Date accessed
[08/05/12] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stop_motion
Date accessed
[08/05/12] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_stop_motion_films
Date accessed
[12/07/12] http://www.adobe.com/devnet/flash/learning_guide/animation/part02.html
Date accessed
[12/07/12] http://www.thebest3d.com/dogwaffle/help/PDHelp/TraditionalAnimation.htm
Date accessed
[12/07/12] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flip_book
Date accessed
[12/07/12] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Traditional_animation
Date accessed
[12/07/12] http://help.adobe.com/en_US/aftereffects/cs/using/WS39e706a46ad531be1172e0812179ce5d44-8000.html
Date accessed
[16/07/12] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drawn-on-film_animation
Date accessed
[16/07/12] http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Movie_Making_Manual/Stills_Photography
Date accessed
[16/07/12] http://graphicssoft.about.com/od/aboutgraphics/a/bitmapvector.htm
Date accessed
[16/07/12] http://graphicssoft.about.com/od/aboutgraphics/a/bitmapvector_2.htm
Date accessed
[16/07/12] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flash_animation
Date
accessed [16/07/12] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anime_Studio
Date
accessed [16/07/12] http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu/collections/toys/html/exhibit07.htm
Date
accessed [16/07/12] http://www.dlt.ncssm.edu/collections/toys/html/exhibit10.htm
Date
accessed [16/07/12] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zoopraxiscope
Date
accessed [16/07/12] http://www.eadweardmuybridge.co.uk/muybridge_image_and_context/zoopraxography/
Date
accessed [16/07/12] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Walter_Elias_Disney
Date
accessed [16/07/12] http://www.justdisney.com/walt_disney/biography/w_bio_short.html
Date
accessed [24/07/12] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Warner_Bros.
Date
accessed [24/07/12] http://www.screenonline.org.uk/people/id/446754/
Date
accessed [24/07/12] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Terry_Gilliam
Date
accessed [24/07/12] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trey_Parker
Date
accessed [24/07/12] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/South_Park
Date
accessed [24/07/12] http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jamie_Hewlett